Sign Languages Display Distinct Ancestries
by Susanne BardWell more than 100 distinct sign languages exist worldwide, with each having features that made it possible for researchers to create an evolutionary tree of their lineages.
Full Transcript
More than 140 sign languages are used today, primarily by deaf communities around the world. Like spoken languages, each sign language has its own grammar, vocabulary and other special features.
For example, American Sign Language and British Sign Language are mutually unintelligible. In fact, American Sign Language has more in common with French Sign Language, largely because French educators were instrumental in helping get deaf schools established in the United States during the 19th century. But while the lineages and development of spoken languages are well-studied ...
“There haven’t been a lot of large-scale comparisons of sign languages.”
University of Texas [at] Austin linguist Justin Power. He and his colleagues aim to address that information gap.
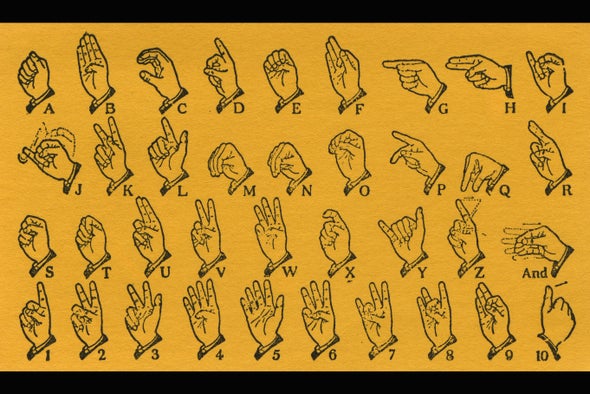
“In order to study the question of sign language evolution, we first assembled a database of manual alphabets from dozens of different sign languages around the world. So a manual alphabet is sort of a subsystem within a sign language that is used to represent a written language. So there’s a hand shape that corresponds to each letter.”
Power’s team chose to study manual alphabets because a record of them exists going back to the late 16th century in Europe. To uncover relationships between the alphabets, the researchers used the same methods that biologists use to trace relationships between different species, based on their DNA.
“The methods grouped sign languages in this study into five main European lineages. And those were Austrian origin, British origin, French origin, Spanish and Swedish.”
Power says manual alphabets from Austria, France and Spain could be traced back to one-handed manual alphabets from 16th- and 17th-century Spain. But each of these lineages evolved independently of each other. And the British lineage, which uses a two-handed manual alphabet, eventually made it to Australia, New Zealand and India.
The study also confirmed the French origins of American Sign Language and those of other countries, including Mexico, Brazil and the Netherlands.
Surprisingly, the Austrian manual alphabet influenced sign languages as far away as Russia. But while this lineage has largely died out, remnants of it live on in Icelandic Sign Language today.
The study is in the journal Royal Society Open Science. [Justin M. Power et al., Evolutionary dynamics in the dispersal of sign languages]
Power says future research comparing the vocabularies of different sign languages could provide even more clues about how they’ve changed over time.
“Understanding how sign languages evolve would tell us a lot about the way that language, in general, evolves.”
—Susanne Bard
[The above text is a transcript of this podcast.]